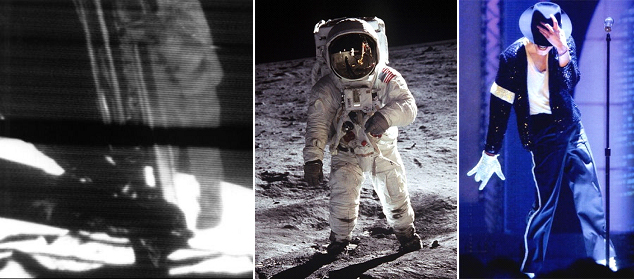
What a pity that Michael Jackson missed the 40th anniversary of the first Apollo moonwalk by only a few weeks.
He was only 10 when Apollo 11’s Neil Armstrong took that historic first lunar step on July 20, 1969 and was probably among the 500 million people — the largest TV audience the world had known at that time — who watched it live. Fourteen years later, Jackson would invent his own kind of ‘moonwalk’.
First performed for his song ‘Billie Jean’ on a U.S. TV show in March 1983, Jackson’s dance technique that gives the illusion of the dancer stepping forward while actually moving backward gained worldwide popularity and became his signature move.
Like that historic ‘moonwalk’ 40 years ago, Jackson’s untimely death on June 25, 2009 created ripples that was felt worldwide. News of his sudden death crashed some news or social networking websites, and stalled others. Even the mighty Google, now the world’s largest media operation, slowed down; Google News was inaccessible for a while.
This is the opening of my latest op ed essay, inspired by the media and public reactions to Michael Jackson’s sudden death. Titled ‘King of Pop Moonwalks to Online Immortality’, it has just been published by the Asian Media Forum website.
I must admit that I’m more a fan of the original Apollo moonwalk than Michael’s version. I was three and a half years when the first Moon landing happened, which remains my earliest childhood memory that can be traced to a specific date.

I look back at how these twin technologies transformed far-away Jackson into a local icon across Asia. I also recall a 2001 documentary named Michael Jackson Comes to Manikganj. Directed by Indian journalist Nupur Basu, it probed how far and wide satellite television was influencing and impacting culture, society and even politics of South Asia. (Full disclosure: I was interviewed on the film, along with nearly two dozen other South Asians.)
Read Nupur Basu’s own recent recollections of how she came across Michael Jackson in remote parts of South Asia, courtesy satellite TV.
The essay ends noting how Jackson could not quite ride the Internet wave the way he did the satellite TV wave. I share my thoughts on how the world’s online population — now over 1.5 billion people according to one estimate — reacted to the news that King of Pop was no more.
The news created a data tsunami of its own on the web, which incidentally – and half the world away – provided a much need respite for the Ayatollahs of Iran…Read the full essay and find out why!
Read earlier blog post: 26 June 2009: Michael Jackson (1958-2009): Mixed celebrity, entertainment and good causes