If one acronym has dominated the world’s media and public minds in the past month, it must be FIFA.
It stands for the International Federation of Association Football, and is derived from the original French name, Fédération Internationale de Football Association. It’s the global governing body of association football, founded in 1904 and with its headquarters in Zürich, Switzerland.
FIFA is responsible for the organisation and governance of football’s major international tournaments — most notably the FIFA World Cup, held once every four years since 1930. The current World Cup, being held in South Africa from 11 June to 11 July 2010, is the 19th edition. The next will be hosted by Brazil in 2014.
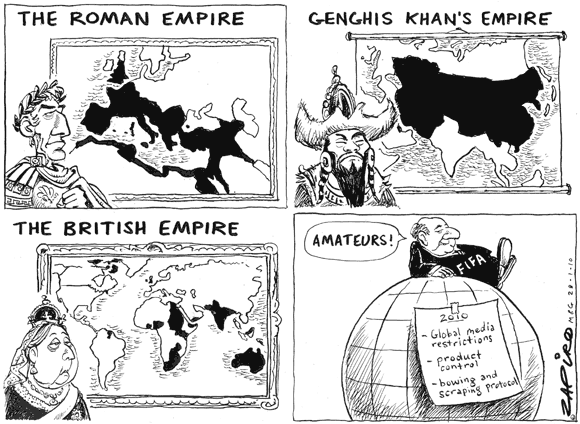
As a global body with substantial financial resources, FIFA has had its own share of controversies and been criticised for its lack of transparency and internal democracy. It’s true that FIFA controls the media rights to key international games with an iron fist (which inspired the above cartoon). They are not alone: the International Olympic Committee (IOC) has its own detractors and allegations on similar considerations.

Indeed, the UN itself is well aware of this. In one of the most memorable op ed essays he’s written, the former UN Secretary General Kofi Annan acknowledged in 2006 (during the previous FIFA World Cup): “The World Cup makes us at the UN green with envy. As the pinnacle of the only truly global game, played in every country by every race and religion, it is one of the few phenomena as universal as the UN. But there are better reasons for our envy.”
He continued: “This is an event in which everybody knows where their team stands, and what it did to get there. They know who scored and how and in what minute of the game; they know who saved the penalty. I wish we had more of that sort of competition in the family of nations. Countries vying for the best standing in the table of respect for human rights, and trying to outdo one another in child survival rates or enrolment in secondary education. States parading their performance for all the world to see. Governments being held accountable.”
Of course, FIFA’s domination over the global public mind will wane after the FIFA World Cup 2010 ends. But how many other global bodies can claim to hold billions of people so engaged for a month? And in this era of 24/7 information society, that’s formidable soft power indeed.
What can we call the wielder of such soft power? How about Super-soft-power?
 And can this kind of power also intoxicate and even corrupt its wielders? We’ve seen how power manipulations work in other centres of soft power, such as Hollywood and Bollywood. The challenge for FIFA — and all others who are connected to it through the love of football and/or media’s outreach — is to watch out that this concentration of soft power doesn’t corrupt.
And can this kind of power also intoxicate and even corrupt its wielders? We’ve seen how power manipulations work in other centres of soft power, such as Hollywood and Bollywood. The challenge for FIFA — and all others who are connected to it through the love of football and/or media’s outreach — is to watch out that this concentration of soft power doesn’t corrupt.
The very same media that helps FIFA attain the status of a soft-super-power needs to keep an eye on how this power is being used. Perhaps that’s the ultimate game in the media-saturated 21st Century: Emperors of Eyeballs vs. Titans of Kick.
Remember, you read it here first.




















