Some films, like certain books, are in the making for years or decades. My latest film, Small Islands, Big Impact, just released online by TVE Asia Pacific, is quite short: slightly under 6 minutes long. But it has been forming in my mind for the past 20 years.
As a science journalist, I have been covering its story since 1989: how the Indian Ocean archipelago of the Maldives – Asia’s smallest country by area and population – is on the ‘frontline’ of climate change impact.
The Maldives packs 325,000 people into a combined land area just under 300 square kilometres spread over 1,192 islands and islets. With an average ground level of 1.5 metres (5 feet) above sea level, it is also the lowest country on the planet. When I first visited the Maldives in late 1988, they were still recovering from a massive storm surge in 1987. Although the damage was limited, the experience showed how vulnerable the Maldives can be to even a small rise in sea levels – this prompted the then President Maumoon Abdul Gayoom to take up the issue internationally. (It was President Gayoom who took up climate crusading at statesman level, well before Al Gore turned up on the scene.)
Interestingly, my first encounter with President Gayoom had nothing to do with climate – it concerned a celestial phenomenon: the Maldives was witnessing an annual solar eclipse and the President wanted to observe it in the company of amateur astronomers from their nearest neighbour, Sri Lanka. So he invited a couple of us over (I was active in the Young Astronomers’ Association of Sri Lanka at the time.)
 I returned to the Maldives in November 1989, that time as a member of the international media covering the first ever small states conference on sea level rise. Held at the Kurumba island resort, it was one of the earliest international gatherings on climate impacts on low lying states, a topic that was to gain public interest and momentum in the years to come. Among the participants were delegates from practically all the small states in different parts of the world (defined as those with less than 1 million population), and scientists from disciplines such as oceanography, climatology, meteorology and geology.
I returned to the Maldives in November 1989, that time as a member of the international media covering the first ever small states conference on sea level rise. Held at the Kurumba island resort, it was one of the earliest international gatherings on climate impacts on low lying states, a topic that was to gain public interest and momentum in the years to come. Among the participants were delegates from practically all the small states in different parts of the world (defined as those with less than 1 million population), and scientists from disciplines such as oceanography, climatology, meteorology and geology.
This was one of the first international scientific events that I covered as an eager young science journalist. I was a foreign correspondent for Asia Technology, a monthly magazine on Asian science and technology published from Hong Kong (now defunct), and freelancing for The Island daily newspaper in Sri Lanka. (There’s nothing online from that coverage as it was in the pre-web era!)
The conference had technical sessions where experts debated scenarios and implications, and a political segment where delegations made their official statements. In the end, they issued the Malé Declaration on Global Warming and Sea Level Rise, which urged for inter-governmental action on the issue.
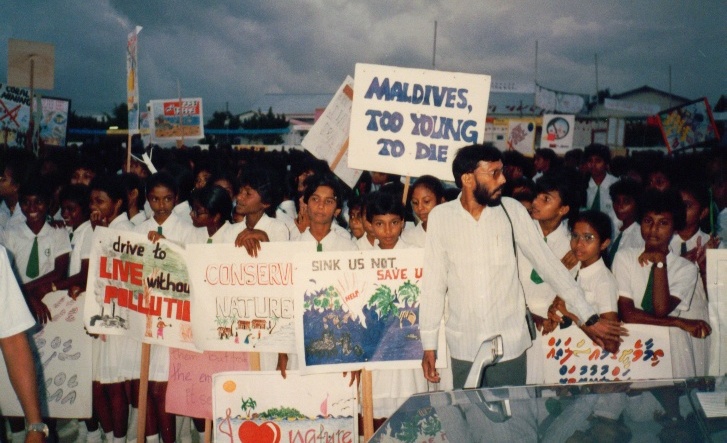
Our Maldivian hosts knew that scientists and officials alone couldn’t send out a powerful message to the world on what climate change meant for low lying islands of the world – many of them mere specks on the world map, barely registering in media’s radar. So on the last day of the conference, we were taken to the Maldivian capital of Malé, where a demonstration and public rally were held by school children and ordinary people.
That turned out to be the most striking moment of the whole week. I had been listening to experts and officials talk about impacts, scenarios and mitigation measures for several days, on which I’d filed several stories. But unless I go back to my personal archives, I can no longer remember those details. My lingering memories of this event are in a few photos I took, showing school children telling delegates – and the world – what it means to be living on the front lines of climate change impact.
This was the most striking photo – three more are found in an earlier blog post:
After 1989, I visited the Maldives on a couple of occasions for professional purposes during the 1990s. After I started working with TVE Asia Pacific in 1996, I was keen to return to the story of the Maldives and climate change – this time, in moving images – but I never had the chance until this year.
But I was covering the bigger story of climate change and its impact on the Asia Pacific from other locations. For example, in 2002, I commissioned and executive produced Voices from the Waves, the first-ever documentary on climate change in the South Pacific made by a native Pacific islander. Directed by Fijian film-maker Bernadette Masianini, the story revolved around two teenagers growing up on Fiji and Kiribati, each facing an uncertain future because of climate change.
In November 2007, the Maldives once again hosted representatives from small island states to discuss climate change. Eighteen years after the original meeting, the subject was no longer a fringe concern; it was now on everybody’s agenda. The meeting urged the the human dimension of global climate change to be included in the agenda of UN Climate Change Summit in Bali (December 2007), and sought the international community’s commitment “to protect people, planet and prosperity by taking urgent action to stabilize the global climate change”.
This time, the Male’ Declaration on the Human Dimension of Global Climate Change called for the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights to assess the human rights implications of climate change and “to conduct a study into the effects of climate change on the full enjoyment of human rights”. It also requested the UN Human Rights Council to convene a debate on human rights and climate change.
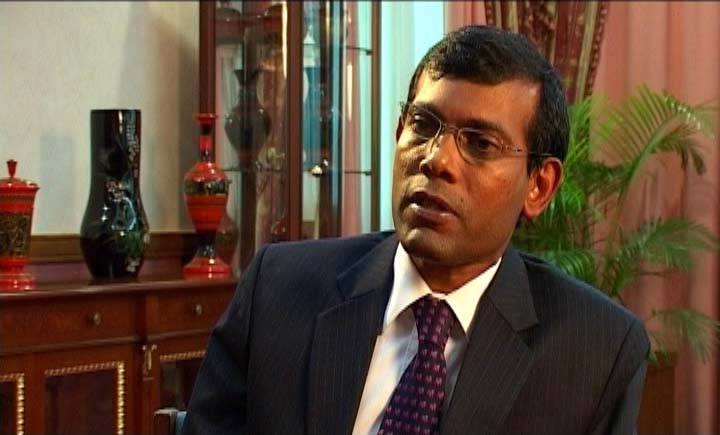
I wasn’t present at the 2007 meeting, but followed the process online. While climate change emerged as a major global concern, political change and reforms were underway in the Maldives. The country moved to a multi-party democracy, and in November 2008, the Maldivian Democratic Party‘s candidate Mohamed Nasheed won the presidential election.

In early 2009, President Nasheed announced that the Maldives would become the world’s first fully carbon-neutral nation within a decade. To accomplish this, they would vigorously pursue renewable energies and green energy sources to replace current dependence on fossil fuels.
The final inspiration for Small Islands, Big Impact came in February 2009, when Science News magazine in the United States carried a cover feature on the challenges faced by Kiribati and the Maldives because of climate change. Written by senior science writer Cristine Russell, the article noted: “The Maldives and Kiribati highlight a hidden challenge for coping with climate change. It’s not just about slowing the emissions of greenhouse gases. It’s also about figuring out what to do for localities threatened with the possibility of extinction from rising ocean waters.”
My original plan was to film interviews with President Anote Tong of Kiribati, and President Nasheed. While sharing the same overall concerns, the two leaders (and their governments) have adopted somewhat different responses to the challenges posed by climate change. Unfortunately, the interview with President Tong did not come through in time, even though I had a Kiribati TV crew standing by to film it. So I decided to go ahead with the film focusing solely on the Maldives.

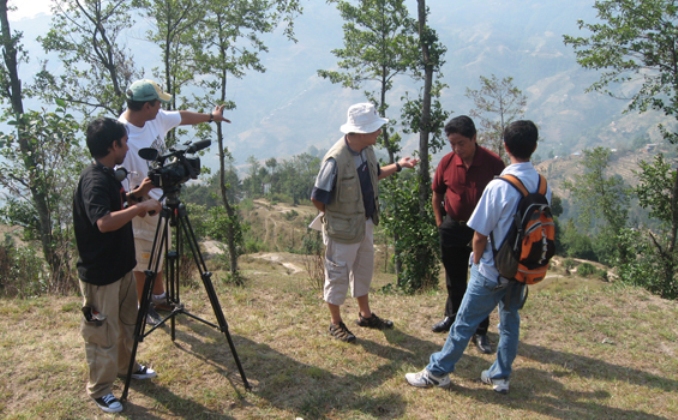
As with all TVEAP films, I was keen to make it with a local crew. Mariam Niuma, an engaging young Maldivian woman who had worked for nearly two years with us as an intern, helped me find a very capable crew in Ibrahim Yasir and his colleague Hussein Makzoom.
Niuma had been urging us to make a film about her country and was delighted that we were finally able to take it up. She helped us in numerous ways with local knowledge, introductions and advice. She also took time off her work with a local charity to show me around the Male’ island – which I was returning after a dozen years, in which time it had changed almost beyond recognition. (Male’ is one of the most crowded places on Earth – every one in four Maldivians lives on the tiny capital island.)
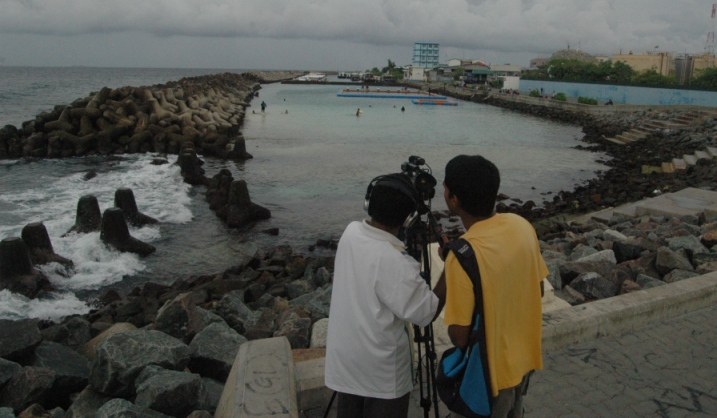
Small Islands, Big Impact was filmed on location over a few days in late August in Male’ and the nearby island of Vilingili. Our tiny production budget didn’t allow us to spend longer or venture further into the more remote islands and atolls (coral island formations, 26 of which make up the Maldives).

President Nasheed’s media team had been quick and supportive in accommodating our interview request, but when actually filming it, we faced an unexpected challenge which I’ve described in an earlier blog post. (Clue: In addition to inclement weather, we had to deal with a nasty influenza virus). With the month-long Ramadan fast period about to begin, which would significantly affect the pace of work in the 100% islamic Maldives, we had no choice but to persist with our filming, improvising as we went along.
I returned to Colombo with five camera tapes rich in footage, one of which contained a 15-minute interview with the amiable and technocratic President Nasheed. Over the next few weeks, I worked with our editor Umesha Fernando in distilling this material into a short, compact film less than six minutes. It took a good deal of time and effort — especially since I chose not to have any narration and to let President Nasheed tell the story in his own voice, interspersed with text-supported transitions.
Because of this style, soundtrack mattered a great deal, and we agonised over custom-composing the music. As I put everything this together, I kept recalling the wise words of senior Australian film-maker Bruce Moir: “Film is a lousy medium to communicate information. It works best at the emotional level.”
In the end, we barely met our self-imposed deadline: the film was released online just in time for the International Day of Climate Action. At the same time, I released the full interview (in text) on TVEAP website and the Groundviews citizen journalism website.
I can’t judge my own film, but I have tried hard to strike a balance between its intellectual and emotional appeal. My team and I set out to tell a compelling story about a country on the frontlines of climate impact. No less a person than its dynamic head of state stars in our modest effort, made on an incredibly tiny budget.
So here it is, a film that has been 20 years in the making – Small Islands, Big Impact!
Note: Small Islands, Big Impact was produced on an editorially independent basis by TVE Asia Pacific in collaboration with COM+ Alliance of Communicators for Sustainable Development. As with all other TVEAP productions, this series comes without license fees, where only copying and dispatch costs are payable. To order broadcast master tapes, please contact:
It may also be ordered in high resolution on DVD (without regional coding) from TVEAP’s e-shop.