The timing of the Third Global Knowledge Conference or GK3 last week just couldn’t have been worse in terms of international media attention and coverage.
Some 1,700 people from all over the world – representing academia, civil society, governments and industry – gathered in the Malaysian capital of Kuala Lumpur from 9 to 13 December 2007 for this platform of events meant for everyone interested in using information and communications technologies (ICTs) for the greater good – to solve real world problems of poverty, under-development, illiteracy and various other disparities that afflict our world.
The organisers, a network called the Global Knowledge Partnership, called it ‘Event on the Future’. They had worked for almost two years on planning the event, and spent a huge amount of development funding to drum up global interest in the event.
As things turned out, GK3 was a complete non-event for the world’s media, whose attention was much more engaged by another event that was crucial for the future of all life on this planet – the UN Climate Change conference taking place in neighbouring Indonesia’s Bali island.
That coincidence of events was very unfortunate, especially since GK3 also discussed and debated important issues that shape our common future. Yes, the substance at GK3 was immersed in — and sometimes buried under — massive volumes of hype and spin, but for the discerning participants there were occasional gem stones amidst the numerous gravel.
I have written up my impressions of GK3 as a series of missed opportunities. In my view, the biggest missed opportunity was GK3’s failure to position itself as part of the smart response to global climate change that scientists now confirm is happening and is largely human-induced.
After 20 years working in the media, I can understand why the news media ignored GK3. Yes, bad timing was one factor. But the bigger lapse was that the GK3 organisers and participants failed to find and articulate their common ground with the bigger global process that was unfolding in Nusa Dua, Bali island.
In the real world, Bali is not all that far from KL. But sadly, the two were worlds apart as parallel processes took place with little confluence.

It need not have been that way. There is much that ICTs can do in reducing carbon emissions that are warming up the planet.
The biggest ‘digital dividend’ from ICTs is how they can help reduce needless travel. Dependent as we still are on fossil fuels of oil and coal for most of our transport, even a few percentage points of travel that we can realistically cut down can yield major savings in emissions of carbon dioxide.
In a blog post written in August 2007, I cited Sir Arthur C Clarke’s slogan that sums this up very well: Don’t commute; communicate!
I quoted from an essay Sir Arthur had written for the UK’s Climate Group in 2005, included as part of a global exhibit on climate issues, where he noted: “….Meanwhile, other technologies enable us to adjust our work and lifestyles. For example, mobile phones and the Internet have already cut down a lot of unnecessary travel – and this is only the beginning. We should revive a slogan I coined in the 1960s: ‘Don’t commute – communicate!’”
My friend and academic colleague Dr Rohan Samarajiva, who heads the regional ICT research organisation LIRNEasia, has given this some further thought.
More and easier use of telecom should theoretically lead to less need to travel. But nothing is ever that simple, he says. “It is not realistic to think that improved telecom-based connectivity will immediately lead to a reduction in demand for transport and a reduction in greenhouse gases. But it is clearly a necessary action that will yield good results over time.”
For telecom to make a real contribution to reducing demand for transport, Rohan says several things need to happen:
• Most people need to have easy and convenient access to telecom, for sending as well as receiving messages and for retrieving as well as publishing information;
• All offices and business establishments must be reachable through telecom;
• They must change their business processes to reduce the need for people to physically come to their locations; and
• The ancillary infrastructures such as energy, payment and delivery systems must change accordingly.
These, then, are important goals that are worth pursuing not only for the achieving information societies but also for saving the planet from the current slow baking. That’s the message that GK3ers failed to grasp or convey to Bali.
Instead, we heard from the movers and shakers of the IT and ICT companies how they are working to achieve greater energy efficiency in the manufacture and use of their products. Their sincerity and commitment were not in question. But I didn’t hear anyone emphatically make the point that helping people to avoid needless transport use is the biggest climate benefit ICTs can deliver. (I was yearning to stand up and say ‘It’s avoided transport, stupid!’ in one plenary but we ran out of time.)
The industry mandarins were not alone. Even the International Telecommunications Union (ITU), which sets standards and keeps an eye on ICT trends and conditions, missed this point. In a statement delivered to the Bali climate conference, ITU talked about lots of small contributions that ICTs can make to find solutions to the climate crisis.
To quote from their 12 December 2007 press release:
“ITU pointed out that the proliferation of ICT products in homes and offices, and their deployment throughout the world, places an increasingly heavy burden on energy consumption. The late night glow in homes and offices emanating from computers, DVD players, TVs and battery chargers is all too familiar. And the move to “always-on” services, like broadband or mobile phones on standby, has greatly increased energy consumption compared with fixed-line telephones, which do not require an independent power source. Energy demands caused by high-tech lifestyles in some countries are now being replicated in others.”
It’s always good to improve energy efficiency, if only to keep the bills in check. But can ICT industry and ITU please stop apologising for the relatively minor contribution their sector makes to global warming — and instead become a much bigger part of the solution? In other words, stop rearranging chairs on the Titanic’s deck, and instead get in the engine room to help steer the planetary Titanic from heading straight into that iceberg looming large.
We don’t need further studies, expert groups or conferences to deliver this category of carbon-saving, climate-friendly benefits: just keep rolling out telecom coverage worldwide and also make the services affordable and dependable. The markets will do the rest.
This point was also lost in Bali. Obsessed as they were with a mechanism to succeed the imperfect Kyoto Protocol, the delegates failed to fully appreciate tried and tested solutions that can begin to roll out now and here. Let the diplomats and lobbysts bicker for years to come, but don’t ignore what markets can do in the meantime.
Even some champions of climate change have yet to realise the ICT potential for their planet-saving crusade. Al Gore, being both ICT-savvy and green, is an exception. Sir Nicholas Stern is not.
In October 2006, the UK government published a 579-page report on the economics of climate change by Sir Nicholas Stern, a former chief economist at the World Bank. Despite the massive size, scope and authority of the report, the Stern Report had no reference to the role that the ICT sector could play in helping to reduce energy demand, mitigate CO2 emissions and help to save the planet.
Fortunately, as I wrote in August 2007, telecom operators are begining to taking note. Among them is the European Telecommunications Network Operators’ Association (ETNO), which issued a report — incidentally, in the same month as the Stern Report — titled Saving the climate @ the speed of light: ICT for CO2 reductions.
It was a joint publication with the World Wide Fund for Nature, WWF. Its introduction read: “A wider usage of ICT-based solutions can play an important role in reducing CO2 emissions. This joint WWF-ETNO road map proposes a concrete way forward for a better consideration and inclusion of ICT’s in EU and national strategies to combat climate change.”
Read the full report here.
So it seems that part of the climate response answer is literally in the air – or the airwaves. The emergence of information societies — where more electrons (carrying information) are moved than atoms (people, goods) — can help the pursuit of climate-neutral or, even better, climate friendly lifestyles. To use a currently fashionable UN term, that’s a co-benefit!
For these co-benefits to be appreciated and seized, it’s essential that we look at the bigger picture and not just work in individual sectors such as ICT and sustainable development. The ITUs and UNEPs of this world have to meet and talk more often — and also listen to each other more seriously.
I chose to attend the ICT event of GK3 in KL in spite of receiving three separate (and sponsored) invitations to join various activities in Bali. After last week, I have mixed feelings about that choice, but there’s no doubt at all in my mind about the massive potential that ICTs hold for mitigating the worsening of climate change.
But the ICT sector has to put its money where its mouth is, and practise what it advocates. It’s not good enough to endlessly meet and talk about all things ‘e’. Just as the world has to kick its serious addiction to oil and coal, we in the development sector have to wean ourselves away from our obsession with paper. Lots and lots of it.
In the last hour of the final day, I walked around GK3’s exhibition area, with the ridiculous name MoO. I was stunned by the massive volumes of paper lying around everywhere. The week’s events were drawing to an end, and it was unlikely there would be too many more takers for all that paper. In that week, I saw very little digital media being used to peddle institutional messages or deliver their logos. It was 95% paper-based.
My colleague Manori captured on her mobile phone this image of an exasperated me surrounded by mountains of paper.
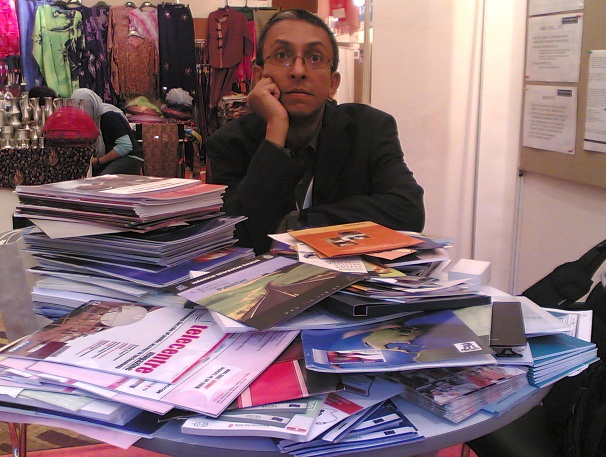

The MoO exhibitors were not alone in their profligacy and wastefulness – the GK3 secretariat easily wins the prize for producing the greatest volume of glossy, expensive paper-based promotional material for at least a year preceding the event.
Clearly both ICT and climate camps have some urgent rethinking to do. Together, we can find win-win, now-and-here solutions for slowing down processes of disruptive climate change already underway.
Or we can keep pushing bits of paper all around, all year round. The choice is ours – and the planet is at stake.
– Nalaka Gunawardene
Read my overall impressions of GK3: All geek but very little meek…and at what high cost?



























